# Use Cases
Cost-Effective GNSS Receiver Testing & Simulation
What is GNSS Testing?
In order to properly test a GNSSGlobal navigation satellite system (GNSS): A general term describing any satellite constellation that provides positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) services on a global or regional basis. See also receiver, or any device or system that relies on global navigation satellite signals, engineers need to simulate the same RF signals that are broadcasted by real satellites.
Test engineers may start with real-world, or “live-sky” tests to see how their new product or device will perform, but it is hard to replicate a test because the satellites are constantly moving. The atmospheric conditions also have variability, and it would be expensive and time-consuming to test a GNSS receiver in all the parts of the globe, and every time of day where it might be used.
Cost-effective GNSS simulation is an extremely helpful and flexible alternative because it allows engineers to recreate GNSS signals and include all the variables for a simulation right at their desk, test bench, or lab. They can then evaluate how their receiver device reacts to real RF signals, how accurate it is, and how it responds to different scenarios, environments, and constellations.
Why is GNSS Testing Important?
It is estimated that 6.4 billion devices in the world rely on GNSS navigation signals – with increasing trends suggesting that this figure could rise to 9 billion devices by 2029.
These types of devices range from a smartphone in someone’s pocket, to a complex flight navigation system inside an airplane or spacecraft. To be effective and ensure the safety of users, technology companies and system integrators are developing methods of reliably and efficiently testing the GNSS receivers that they use in their systems and the possible scenarios that could occur.
Of course, there are different grades of GNSS testing depending on your needs. For example, the testing required for a mobile device will not be as complex or rigorous as the testing needed for aerospace vehicles or resilient systems.
How Safran GNSS Simulators can Help
When it comes to GNSS simulators that generate the same RF signals broadcast by global (and regional) navigation satellites, Safran has cost-effective solutions for all budgets and needs.
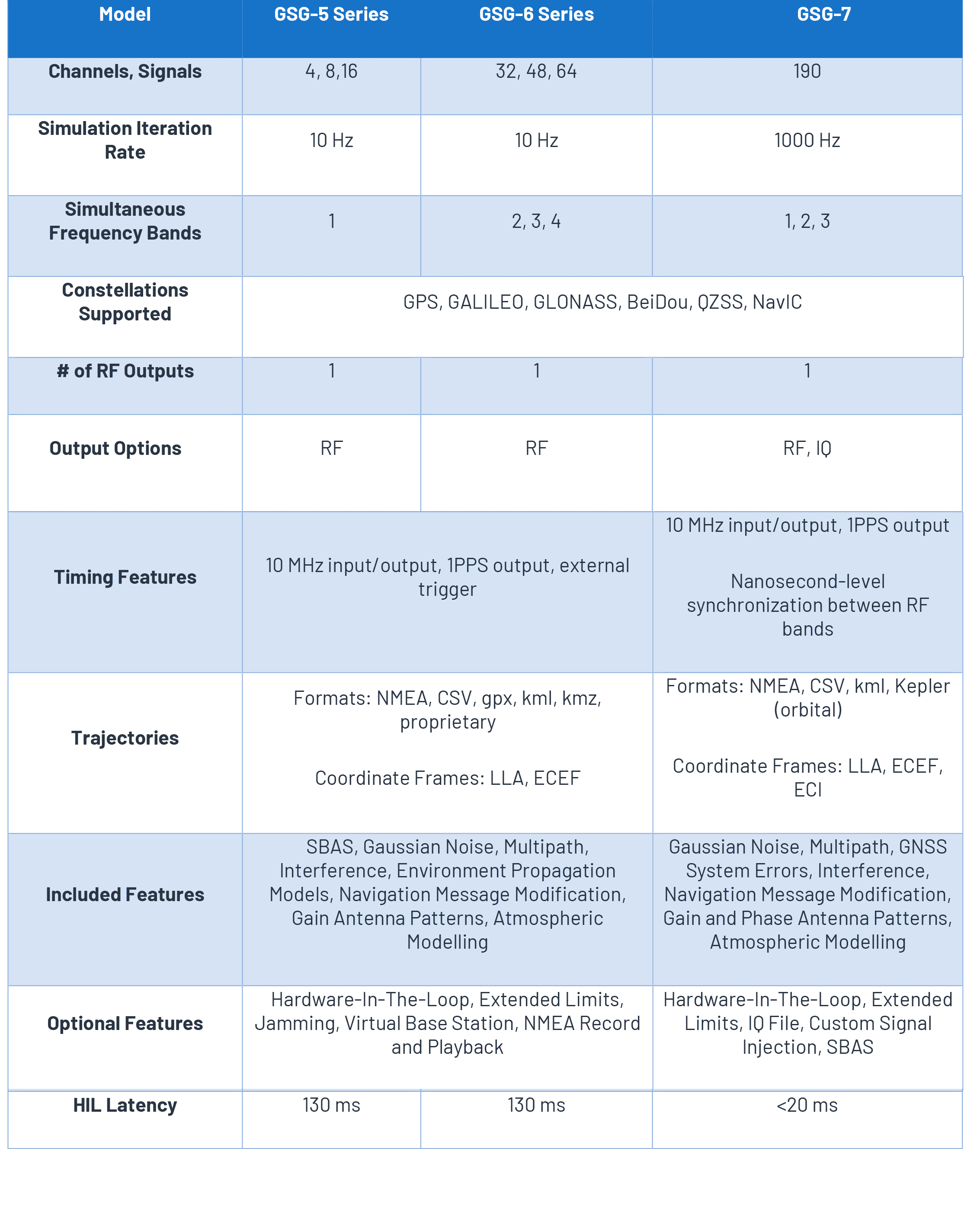
GSG-5/6
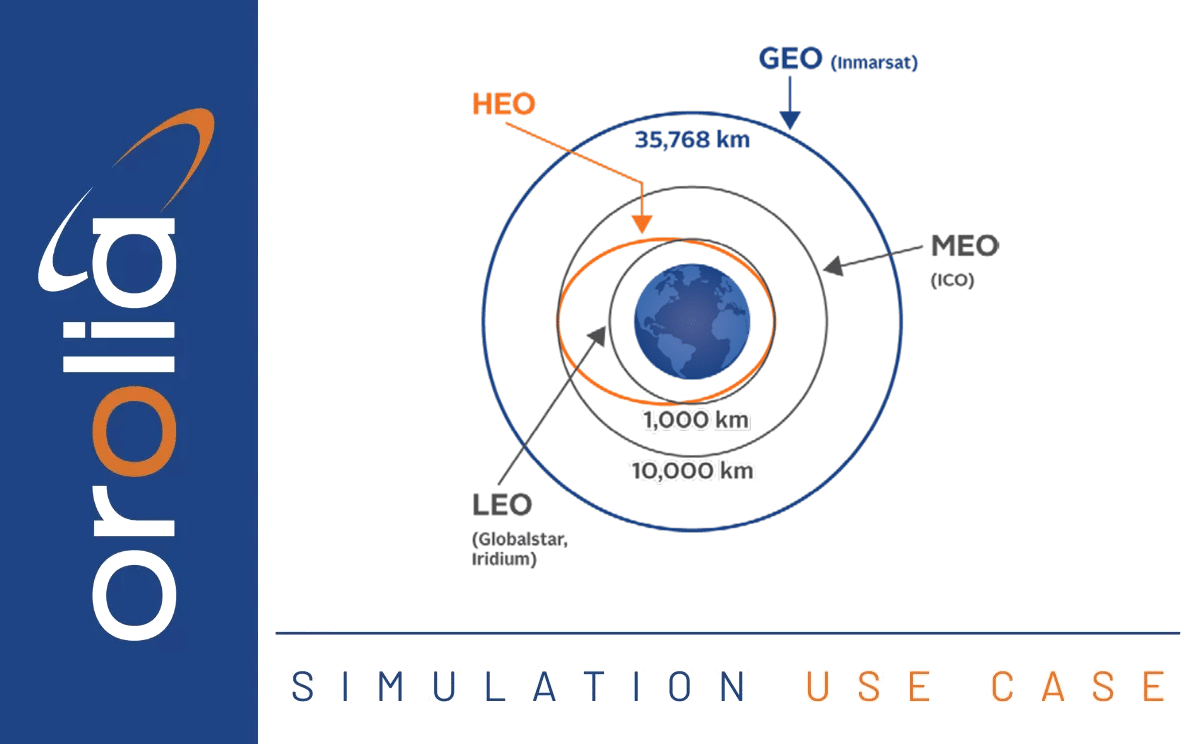
Safran’s GSGA GNSS Signal Generator is a device that is able to create simulated satellite signals and generate real RF signals by first producing I/Q data and calculating the orbits of satellites at a user-defined time, location and trajectory. 5/6 Series Simulators can simulate all the major GNSS constellations that you may need for your testing, including GPSGlobal Positioning System is a navigation satellite system. See also, GLONASS, GALILEO, BeiDOU, QZSS and SBAS – all through a single RF output.
The lightweight form factor means that you can conveniently place a GSG 5/6 simulator on your desk and or transport it easily to your office or testing lab.
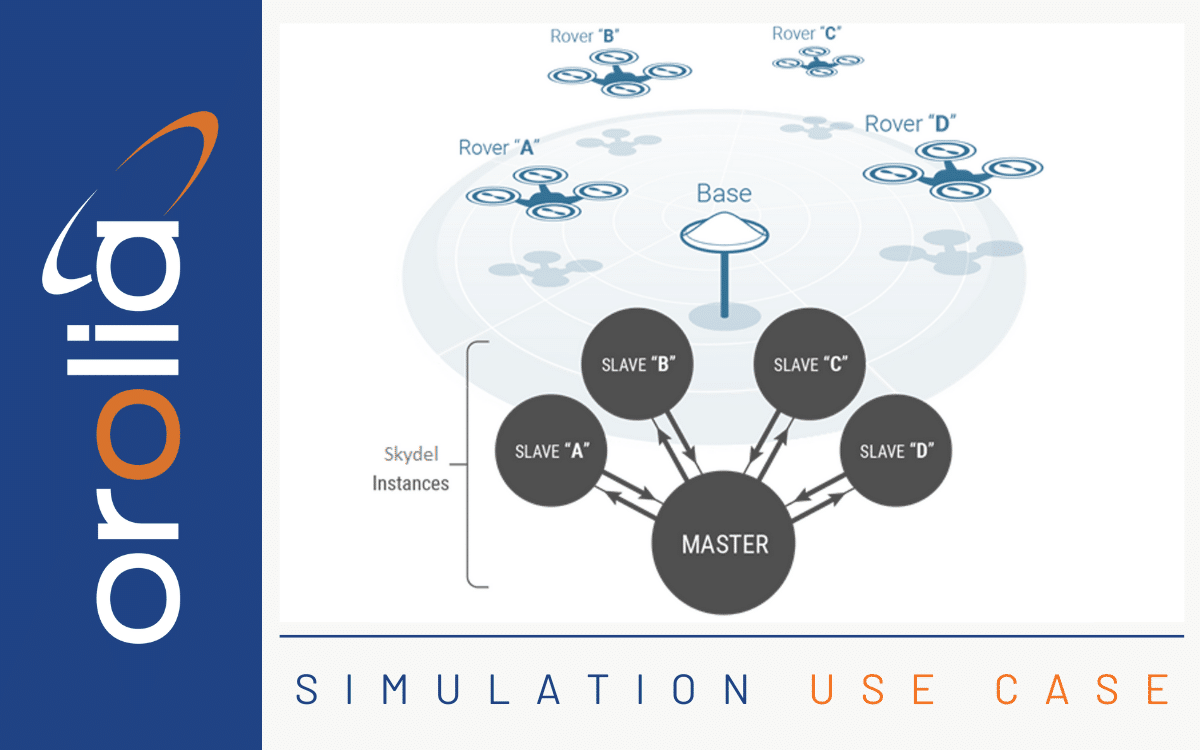
Both the GSG- and GSG-6 simulators can generate up to 64 simultaneous satellite signals that correspond to any position on or above the Earth. This gives you flexibility to create an unlimited number of test case scenarios that are relevant to your system and use-case.
GSG-7
The newest member of Safran’s GNSS simulator family, the GSG-7 is a turnkey, easy-to-use, cost-effective hardware platform that is powered by the Skydel simulation engine. It is ideal for development and integration projects that require high performance and an increased number of constellations.
With a reduced form factor (U2), the GSG-7 is a rack-mounted, robust simulator that features high-end performance with a 1000 Hz simulation iteration rate, high dynamics, real-time synchronization, and simulation of all-in-view satellite signals.
The GSG-7 GNSS simulator is powered by the Skydel simulation engine, which brings an arsenal of benefits including support for multi-constellation and multi-frequency simulations, comprehensive API, robust yet simple automation, and low latency Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL).
Ease of Use:
- Conveniently modify parameters of each simulation on the front panel. No need for superfluous serial connections and add-on utilities.
- Designed so that even inexperienced operators can configure scenarios on the fly without the need for an external PC.
Why Choose a Safran GNSS Simulator?
- Powerful – Create an unlimited number of user-defined scenarios.
- Flexible – The GSG 5/6 GNSS Simulators can be controlled either via an Ethernet Network Connection, USB, GPIB, or using a web user-interface where you can control the unit and the settings on the front panel.
The GSG-7’s intuitive interface includes an extensive API, and automation tools that allow users to instantly record and export interactions. - Easy-To-Use –Users can easily change the date, time, position, trajectory, number of satellites, satellite power levels and atmospheric models with the buttons on the front panel (GSG-5/6) or in the Skydel interface (GSG-7).
- Powerful – Create an unlimited number of user-defined scenarios and reconfigure them on-the-fly (GSG-7 only).
- Lowest-Cost-Of-Ownership – All Safran GNSS Simulators are competitively priced because they were designed to help test engineers quickly and efficiently test GNSS receivers. In addition, the GSG-7 leverages COTS SDRs and GPUs which, in addition to being cost-effective, permits easy customization and mainetenance.
If you need to test dynamic conditions, for example, the movement of your receiver device over a given area, either StudioView™ (GSG-5/6) or Skydel (GSG-7) software gives you an easy way to define the trajectory of your receiver that is being tested.
Both softwares let you easily create and edit scenario parameters. You can convert trajectories that you created in other programs from KMLs, KMZs and GPX files and turn them into NMEA data. Most importantly, the intuitive graphical user interface allows you to use real maps to configure your simulation scenarios.
Request A Quote Or Information
 Related Resources
Related Resources
Related Resources